What Does ARV Mean in Real Estate Investment?

One of the most important figures that real estate investors must know is After-Repair value (ARV). Determining whether multi-family housing or commercial real estate is worth rehabbing is essential.
What is ARV in Real Estate Investing?
After-repair value estimates a property’s value after all planned renovations and repairs are completed.
ARV helps real estate investors determine how much a property could be worth. From that, they can decide on a purchase price, renovation and repair budget, and ultimately, whether a property is worth investing in.
Essentially, ARV is the estimated market value of a property after it has been fixed. The work could be anything from major structural repairs to smaller details like new appliances.
Answer a few questions and get custom mortgage quotes. We'll match you with offers from our network of 650+ lenders.
Key Factors Influencing ARV
Real estate investors should know that after repair value is only an estimate and not guaranteed. Multiple factors could impact ARV, either when calculating the figure or afterward. Some of the most important ones to be aware of are:
- Purchase Price: The value of repairs is added to the purchase price when calculating ARV. Thus, the purchase price has a direct and large impact.
- Repairs Made: There’s no standard amount of repairs and renovations that must be made when flipping a property. The extent of work and type of work, thus, have a direct impact on ARV.
- Market Fluctuations: ARV is estimated based on current market conditions, not taking into account appreciation because holdings are usually short-term. Even during the short term, however, market conditions can change so that the actual value realized post-repairs increases or decreases.
- Assumptions and Opinion: Any ARV figure is calculated by an individual (often an appraiser or investor). Their assumptions and opinions must be accurate for an ARV to be accurate. This is why local expertise and experience are valuable when estimating ARV.
Anytime repairs or renovations are being made to a property, especially one that’s a fixer-upper, unknown issues could arise. Repairing unknown issues won’t add to the ARV of a property, but they’re potential expenses that investors need to budget for.
Why is ARV Important for Real Estate Investors?
Real estate investors who focus on flipping properties need to understand ARV in order to estimate how much a property could be worth after fixing it up. Decisions on purchasing, offer price, and what work to do can only be accurately made after estimating ARV.
Investors who already have a long-term holding should consider ARV in two cases. First, it should be calculated anytime major repairs or renovations are being planned. Investors should know the expected return on investment (ROI) of the work they’re doing, even if they are holding the property long-term. Second, investors should consider ARV before selling a property.
They may find that certain repairs will substantially increase ARV more than the cost of the repairs or that other repairs aren’t worth doing because they won’t increase ARV enough.
How to Calculate After Repair Value: ARV Calculator
ARV is calculated based on the purchase price and the value of repairs/renovations. This number should be based on and confirmed with accurate comparables.
ARV Formula & Examples
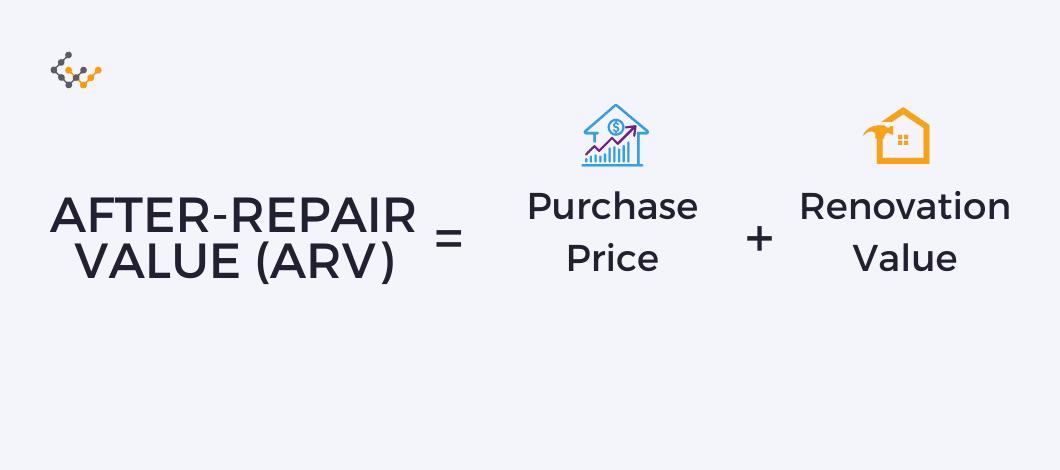
The formula for ARV is straightforward:
After Repair Value = Purchase Price + Renovation Value
To see how ARV might be calculated for different types of properties, consider the two examples.
The first is a basic 5-unit residential property in poor condition. One unit shows severe tenant damage, another has a water problem, and the remaining three haven’t been updated in at least ten years. Many repairs are needed.
An offer price of $1,500,000 is proposed for the property. Assuming that all repairs are undertaken, they have the potential to increase the property’s value by $300,000 (an average of $300,000 per unit). Consequently, this would elevate the After Repair Value (ARV) of the property to $1,800,000, which is the sum of the $1,500,000 offer price and the $300,000 added through renovations.
The second is a commercial shopping center that’s in good condition, but there’s not enough traditional retail demand to keep the property fully occupied. It’s to be renovated with office space, a small live theater stage, an escape room, and a dog training area.
These renovations won’t cost much but could add $500,000 to the property’s value. An offer of $750,000 is made, resulting in an ARV of $1,25 million ($750,000 price + $500,000 renovations = $1.25 million ARV).
What is the 70% Rule?
The 70% rule is a reasonably standard ratio investors and lenders use when evaluating properties for flipping.
The rule states that no more than 70% of the ARV should be put toward purchase and repairs. In other words, investors should look for a 30% ROI on their investment in a property. Such a margin provides a buffer for unexpected repair costs, project delays, market changes, and other challenges while still maintaining a respectable amount of expected profit.
As with any rule in real estate investing, the 70% rule isn’t a hard-and-fast rule in every situation. It is a widely used ratio that most investors and lenders will look at, though.
How to Use After-Repair Value
After repair, the value is most useful in conjunction with the 70% rule, investors and lenders use it in two main ways.
Investors can use ARV and the 70% rule to determine a maximum purchase price. The maximum purchase price should be 70% of the ARV, less all estimated repair costs.
Maximum Purchase Price = (ARV x 70%) – Estimated Repair Costs
Lenders use ARV and the rule to determine the maximum loan amount. The maximum loan permitted is usually 70% of the ARV, effectively a 70% loan-to-value (LTV) ratio based on the post-repair value.
Maximum Loan Amount = ARV x 70%
Wrapping Up
Anytime you plan on selling a property, make sure you conduct an ARV calculation. You’ll be doing this regularly if buying and selling properties or perhaps periodically if renovating or selling longer holdings. Either way, ARV and the 70% rule will help you better ensure your repair and renovations will likely provide a substantial positive ROI.